|
The spin wavefunctions must be symmetric of anti symmetric with
respect to the interchange of the nuclei. It is evident that the
first two functions are symmetric but the latter two are neither
symmetric or anti symmetric since a change of label does hot yield
the wavefunction multiplied by -1
From these, two wavefunctions, linear combinations can be made
that are either symmetric or anti symmetric to exchange of the labels.
Q4.9 Write down the 4 normalised spin wave functions for the 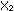 molecule.
molecule.
Q4.10 Explain the meaning of the words -ortho and -para in this
context.
Q4.11 How do these spin wave functions affect the shape of the spectrum
for 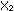 ? ?
|